What Is a Skin Lump? Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
What looks like a single, gigantic blackhead on the outside actually hides a super dry and aged CYST that looks like a… bulb of garlic or mashed potatoes?! Share your thoughts in the comments below. 😮 Do You Have a Lump, Bump, Spot or Skin Condition?
The term “skin lump” may be vague — and the symptom can stem from many causes. By decoding how it feels and looks, you can gain some clarity about what’s going on, gain peace of mind, and work out how to move forward with treatment (as well as whether you even need to).
“When patients complain about lumps, it usually refers to something on the skin that feels elevated or something under the skin that elevates it,” says Lucia Seminario-Vidal, MD, PhD, a board-certified dermatologist at USF Health Morsani College of Medicine in Tampa, Florida.
Skin lumps can have many causes that affect how they look or feel. The following are some signs and symptoms that define a skin bump, says Rebecca Hartman, MD, MPH, a cutaneous oncologist at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston. Keep in mind that a single lump can’t match all the descriptions on this wide-ranging list.
- A lump that feels soft, mushy, or squishy
- A lump that feels mobile
- A lump that’s fixed
- A firm lump
- A lump that feels hard
- A lump that’s red and inflamed
- A painful lump
- A lump that has a central pore
- A lump that looks well-defined under the skin
- A lump that has an irregular contour
- A lump that is growing
A “skin lump” is a specific symptom of a medical condition, so the cause behind it depends on exactly what the skin lump is.
- Benign: The lump is noncancerous and may not require any treatment.
- Inflammatory or infectious: The lump requires treatment but is not life-threatening.
- Malignant: These are cancerous and would require treatment in the short-term (rather than a wait-and-see approach).
Skin Tag

This bump is still worth mentioning here. These often appear in areas of irritation or where skin rubs together, like the neck or armpit, says Seminario-Vidal. These are benign. They’re more common after age 40, and can happen to anyone, but are more likely to appear on people who are obese, have diabetes, or have a family history.
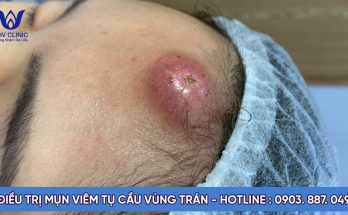
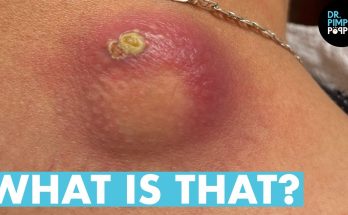
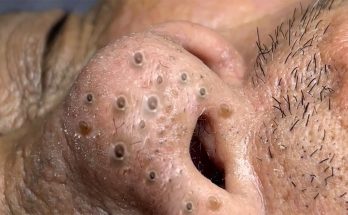
Cyst

This is one of the most common causes of a skin lump, says Dr. Hartman, and they often appear on the face or back. “These are smooth and mobile, are oval with a defined border, and they aren’t entirely squishy, but they’re not firm and hard either,” she explains.
This happens when skin does not mature properly and folds into itself, forming the pore. Dr. Hartman advises that not all cysts will have a visible pore. Cysts might become red and painful or secrete fluid if inflammation or an infection develops. If you suspect you have an infected cyst, seek medical care.
Wart

More than 100 different types of HPV can pass between humans, and they don’t cause symptoms in most people.
They are contagious, meaning that contact with a wart can transmit HPV. The most common type of wart has an almost cauliflower-like appearance.
Dermatofibroma

They look like a small, red raised bump and are firm and “rock-like.” They do not have a known cause.
Rarely, a dermatofibroma may turn out to be a dermatofibrosarcoma after further examination, which is a type of connective tissue cancer that looks like a cluster of lumps on the skin.

Lipomas can develop anywhere on the body. “It can run in families, so there may be a genetic cause,” says Hartman.
These are typically not painful but can cause pain if they press on nearby nerves.
Enlarged Lymph Node

These can swell if you get sick, as immune cells gather there to fight off an infection. Common infections that lead to swollen lymph nodes include strep throat, measles, ear infections, a dental abscess, mononucleosis (mono), skin infections, and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
Seminario-Vidal adds that lymph nodes in the groin may also enlarge and become inflamed due to extreme exercise, such as participating in a long endurance event like a marathon. You should seek medical attention if your lymph nodes feel or appear swollen.
Your dermatologist can perform a physical exam to diagnose your skin lump. If they note something concerning (for example, a skin lump or bump growing), they will likely recommend a biopsy, says Seminario-Vidal.
A dermatologist can take the biopsy depending on the lump’s location or how deep it is under the skin. In areas where the skin is particularly thick, like the back, a plastic surgeon may have to open up the skin under local anesthesia, she says. If the lump is extremely deep, an individual may need general anesthesia for the biopsy.
Prognosis of Skin Lumps
The outlook of a skin lump depends on the cause and whether it is benign, potentially cancerous, or cancerous. “When patients notice a lump, they’re often understandably concerned, but most are benign,” says Dr. Hartman.
Benign:
- Skin tags
- Cysts
- Lipoma
- Warts
- Dermatofibroma
- Enlarged lymph node, if caused by a viral infection, like the common cold
Possibly cancerous:
- New, changing, itching, or bleeding spot, lesion, or bump on the skin, which could point to a nonmelanoma or melanoma skin cancer
Cancerous:
- Dermatofibrosarcoma
- An enlarged lymph node, if caused by lymphoma, or cancer of the lymph system
But even people with cancerous skin lumps can improve their outlook if they seek treatment before it has a chance to spread. The outlook for cancers that cause skin lumps, including lymphoma, depends on:
- The type of lymphoma
- A person’s age
- A person’s overall health status
How long skin lumps stick around and recovery time completely depends on what has caused the skin lump and whether removal is necessary.
A red, painful inflamed cyst may shrink over a few days as inflammation subsides,
but a cyst will need treatment if the patient would like to get rid of it permanently, says Hartman.
Sometimes, Hartman may suggest leaving a cyst alone if the location of the lump, such as the face, means that treatment could be more disfiguring than the cyst itself. Surgeons also typically do not remove lipomas, adds Hartman, unless they are large, growing, or bothersome.
Many skin lumps won’t resolve without treatment. Often, however, the lump is not dangerous and does not need treatment if it does not cause functional problems.
Skin Tag Skin tags are benign and do not need to be removed, but a dermatologist removes skin tags using one of three methods:
- Snip excision
- Cautery
- Cryosurgery, or the use of a cold liquid, like liquid nitrogen, to freeze the skin tag
Cyst Removal is necessary to get rid of a cyst, says Hartman. She advises against taking matters into your own hands. “I tell people not to pop them. Squeezing it may press out keratin, but that does not eliminate the problem and may make it worse by causing more inflammation,” she says.
They may delay surgery if the cyst shows signs of inflammation.
Doctors can also drain cysts as a temporary solution and give a cyst a steroid injection to help calm the inflammation.
At home, you can use an over-the-counter wart removal kit that includes salicylic acid.
At the doctor’s office, they can freeze off warts with liquid nitrogen.
If dermatofibrosarcoma develops, surgery can remove it, although a doctor may also request radiation or targeted therapy drugs to destroy any cancer cells that remain after surgery.
The minor procedure requires an injection to numb the area but takes just 30 minutes, she says.
Enlarged Lymph Node You don’t need to treat an enlarged lymph node itself, but treatment is necessary for the underlying cause. If lymph nodes have swollen because you have a viral infection like a cold, they should return to their standard size once you recover, says Hartman. That said, if you find an enlarged lymph node that’s 1 centimeter (cm) or less in diameter, it’s soft, and you can move it around, that’s less concerning, says Seminario-Vidal. Doctors may take a wait-and-see approach and follow up to make sure it’s gone down.
Integrative and Complementary Approaches
For many lumps, there is little you can do at home. But a warm compress on a red and angry cyst can relieve inflammation and ease soreness, says Hartman.
None of the homeopathic remedies are effective, and warts should resolve without treatment once the body develops an immune response.
Skin tags aren’t always preventable, as they can have genetic causes. But controlling conditions like diabetes and obesity that increase the risk of skin tags will discourage their formation.
This is achievable through body weight management and effective blood glucose control.
Most benign skin lumps are not harmful, says Hartman. However, she maintains that skin tags, cysts, and lipomas can become bothersome on visible areas like the face, catch on clothing, or develop inflammation and tenderness.
Trying to drain or remove a skin lump at home risks complications like bleeding or infection.
“Skin lumps” are a common symptom. Here are some statistics related to various types:
You can get them at any age, but they are more likely in adults aged 40 to 60 years.Clinic.
Lymphoma In the United States, around 4% of people with cancer have non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), making it one of the country’s most common cancers.
The American Cancer Society predicts that about 80,620 people will receive an NHL diagnosis in 2024.
Men account for more NHL diagnoses than women.
Resources We Trust
- Mayo Clinic: Lymphoma: Symptoms and Causes
- Cleveland Clinic: Skin Cancer
- American Academy of Dermatology Association: Skin Tags: Why They Develop, and How to Remove Them
- Skin Cancer Foundation: Amelanotic Melanoma: It Doesn’t Look Like Other Melanomas
- InformedHealth.org: What Are the Treatment Options for Warts?
Skin lumps take many forms, but the vast majority are noncancerous. Skin tags, lipomas, and cysts only need treatment if they’re causing significant problems, and warts tend to heal by themselves over time. Enlarged lymph nodes can point to an underlying infection or disease but tend to resolve when a person manages the disease, and dermatofibromas are generally benign.
Swollen lymph nodes may sometimes point to lymphoma, but treatment can help to send the disease into remission or cure it completely. If lumps are causing concern, seek a clinical opinion — even if the lump is harmless, it’s best to rule out anything more serious.